- Overview
- Transcript
4.4 Contributing and Contributors
1.Introduction3 lessons, 16:39
1.1Introduction02:59
1.2Installing and Configuring Git08:00
1.3Git Concepts05:40
2.Git Basics5 lessons, 40:43
2.1Initializing a Repository07:05
2.2The Staging Area and Status Command05:12
2.3Making Commits10:34
2.4Ignoring Files08:06
2.5Viewing the Log09:46
3.Branching and Tagging5 lessons, 36:16
3.1Creating Branches08:02
3.2Fetching and Pulling09:20
3.3Diffing Files05:13
3.4Merging Branches07:03
3.5Tags06:38
4.GitHub and Remotes4 lessons, 39:34
4.1Setting Up GitHub10:42
4.2Working With Remotes10:12
4.3Creating GitHub Pages11:57
4.4Contributing and Contributors06:43
5.Intermediate Usage3 lessons, 22:04
5.1Stashing Changes10:45
5.2Cleaning Up Merge Conflicts03:46
5.3Rebase07:33
6.Conclusion1 lesson, 01:16
6.1Conclusion01:16
4.4 Contributing and Contributors
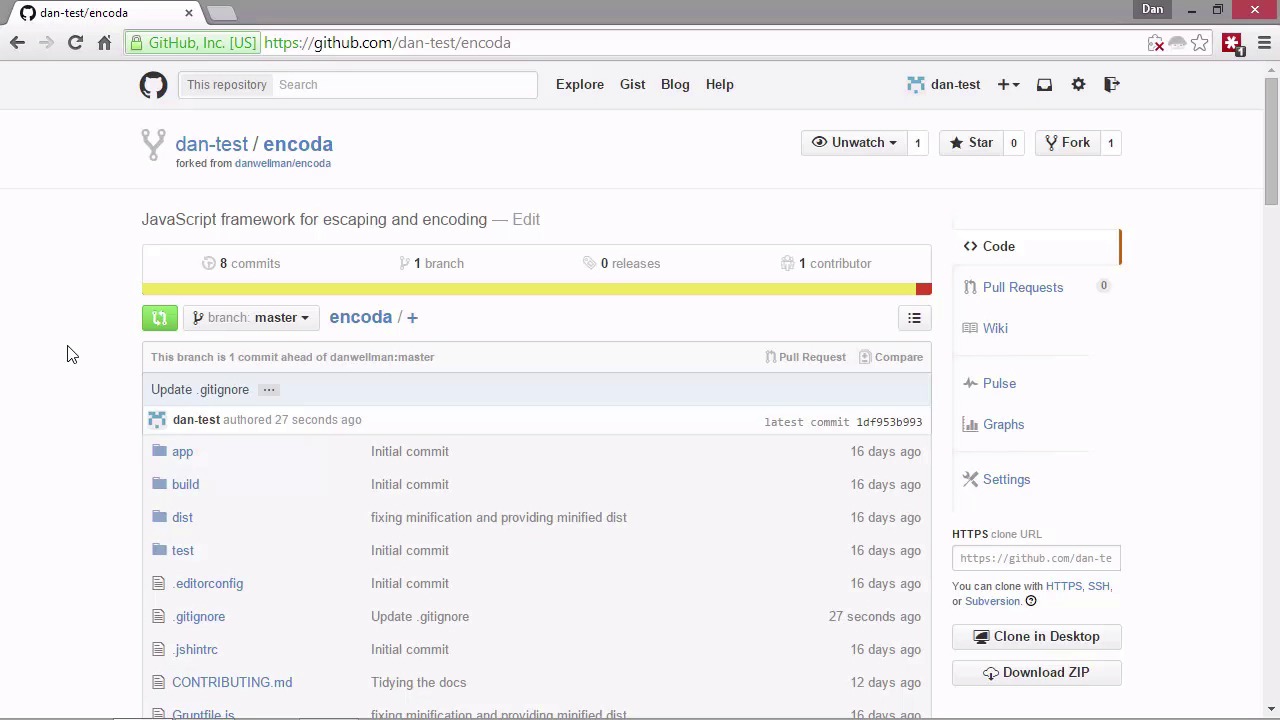
Hi, folks. In this lesson, we're gonna look at a very important aspect of GitHub. And that is contributing to other repositories and handling contributions from other people. Sharing code is one of the big pluses of GitHub, so these are good things to learn early. So let's look at contributing to other repositories first. This could be the reason why you wanted to learn Git in the first place after all. To contribute to an open source framework, or library. So lets go back up to GitHub. [BLANK_AUDIO] So we need to find a repository that we'd like to contribute to. Remember earlier in the course that I mentioned I already have a personal GitHub account. Well, I've got a library here on my regular GitHub account, so let's see how we would contribute to that. [BLANK_AUDIO] So, this is my main GitHub account. I'll just go danwellman and the framework or library that it will fit together is called encoda. That's not important. What is important is that when we want to contribute to another person's repository, the first thing that we have to do is fork that repository. So up in the header here, you can see that there's a button called Fork. I'm just gonna click on that, and that will start the process of forking off. So we're still in the dan-test account, and it's come back to my account now. I'm no longer looking at my other account's page. And you can see that we've got a complete copy of this other repository. So forking means basically that we want to take somebody else's repository in order to make changes to it. So we can now clone this down to our own computer and update the files, run any of the unit tests, and do whatever we need to do in order to make a contribution. Usually in people's repositories, there's a file called contributing.nd. And that is where the author of the library or framework will tell people what they expect. So I've got one here. Let's just click on that and take a look. And it's just a simple mark down file. And it tells people what the code style should be, how to run the tests, that kinda thing. So I'm not actually gonna worry about cloning this down to my computer. We can make a change to one of the files in the repository, and we can do that through GitHub itself. So let's find a file, and we can just update that. Let's just add something to the Git ignore file. And when we're looking at the contents of the file, you can see that there are several buttons here. One of these is an edit button, I'm just gonna click on that. And let's just add something else to ignore. And let's just say there's a type of file called a .test file, and we are gonna ignore that. So we need to save that now. By default GitHub adds this update.ignore description for us, but we can add an option or extend the description if we want. So let's just put. So we added something to ignore.test files and we got a couple of options here we can create a new branch for this commit. Or we can just commit directly to the master branch. Let's just commit directly to the master branch and we'll use the commit changes button. So that's now committed. So let's now go back to the main page of our fork, and next to the branch button you can see that there's a green button that has two arrows on it. This is the button that we clicked in order to start making a pull request. And a pull request is how we actually get changes that we make into somebody else's code. So we click on that and that takes us to this page where we can create the pull request. And that shows us exactly what file was changed and it shows us a diff so that we can see what the changes actually were. So let's click on the create pull request button now and we've got a chance to update the description or the title. But, I'm not gonna do any of that now. So, I just wanna draw your attention over to the right-hand side of the page here, we've got this big green icon and a tick. And it says that we are able to merge straight in with this change. So that basically means that there's been no other commits or changes in the, in the original repository that we forked since it was forked. And so if the owner of that repository chooses to, they can merge this straight back in, and it will be nice and easy and quick for them. So let's now click the Create pull request button down at the bottom right here. And we just get a little status page here, and this is the update page for this file. So, I'm going to sign out of this account now and sign in with my main accounts. And then we can look at how to handle contributions from other people. So as soon as I sign in I can see that I've got a notification and there's some activity on my feed. And if we go to the notifications area it says oh somebody has updated the .gif ignore and there's an avatar of the person who did that. I'm just going to click on that so that we can go straight to it. And we go back to this page now. It says dan-test wants to merge one commit into Dan Wellman code on master, and it just comes from dan-testmaster. So those are the branches that need to be merged. And there's some information here about the comment that was left, and we can see how many commits there were, and how many files we changed. And, if I wanted to bring this change into my library, I could just click on this merge button here, and that would happen straight away. I'm not actually gonna do that, so what I'm going to do now is close this pull request, and I'm just gonna leave a message here, just to say. [BLANK_AUDIO] I don't want this in my library, and I'm gonna close the pull request now. So no action was taken. We can see there's a red icon with a stop sign in it and that means that the pull request has been closed. So now I'm gonna sign back out of this. I'm gonna sign back in with my test account. And I've also got a notification here, so let's go and take a look at that. It tells us straight a way that the merge icon is red so that this pull request wasn't actually merged in. And if we go into that now we can then see the message left by the owner of that repository. They don't want this in my library. So in this lesson we saw how to be a contributor to other people's repositories, which is something that we're strongly encouraged to do. We also saw how to manage pull requests from other contributors to our own repositories. Which is a skill you'll need if you create a popular project that lots of people want to work on. Thanks for watching.