- Overview
- Transcript
2.3 Grouping Routes with app.route
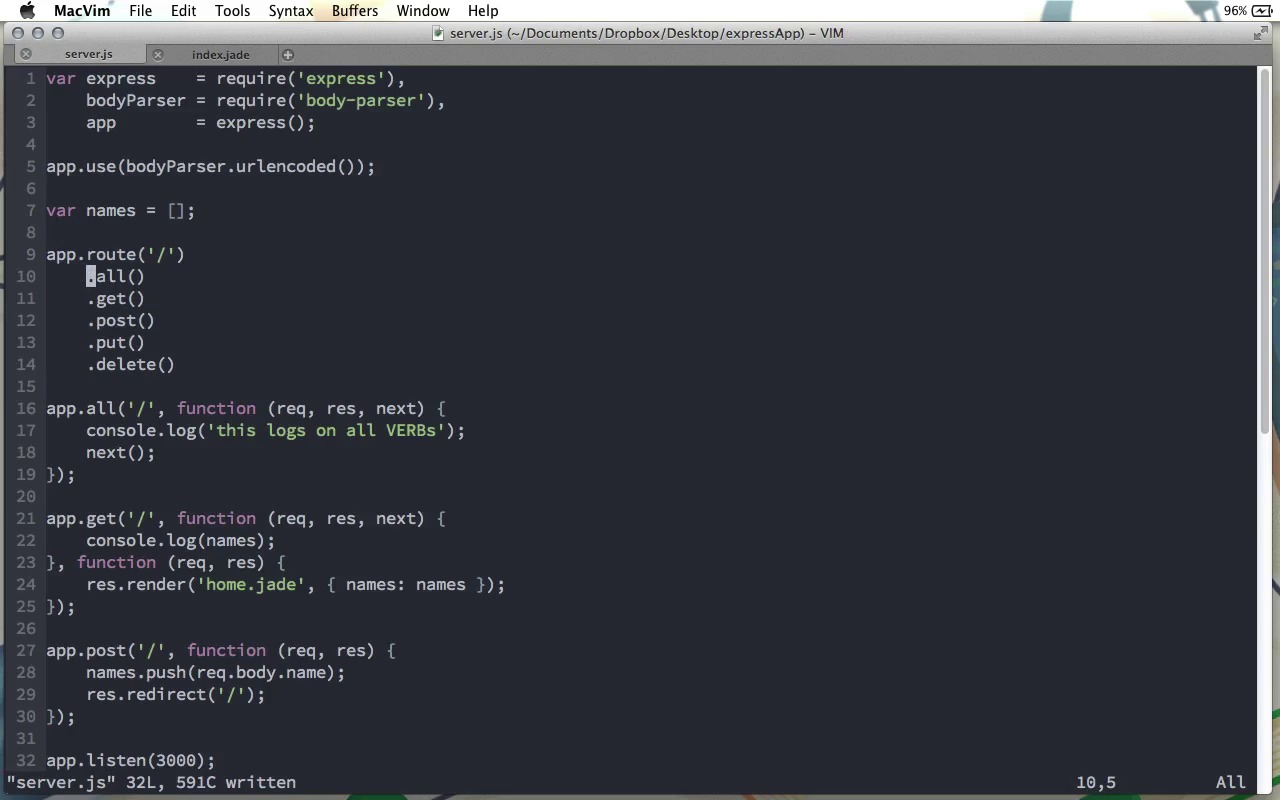
We’ve looked at the verb methods already. Often you’ll want to have several route functions for the same path, but with different verbs. That’s easy enough, but it’s a shame to have to repeat the route string over and over. In this lesson, we’ll look at the app.route method, which allows us to remove this duplication.
1.Learning the Basics of Express6 lessons, 33:03
1.1Introduction01:09
1.2How to Install Express 401:11
1.3Your First Express Application04:09
1.4Views and Templates07:37
1.5The Verb Methods09:10
1.6Application Settings09:47
2.Understanding Request Flow in Express4 lessons, 20:09
2.1Middleware and Request Flow06:25
2.2Custom Middleware Based on Route Parameters04:59
2.3Grouping Routes with app.route02:46
2.4Router Objects05:59
3.Request and Response Objects3 lessons, 11:11
3.1Request Object04:13
3.2Response Object04:15
3.3Formatting Requests02:43
4.Conclusion1 lesson, 01:35
4.1Conclusion01:35
2.3 Grouping Routes with app.route
In this screencast, we're going to look at some new shortcut syntax that Express offers for making our route definitions a little bit tighter. We're gonna start with the code that we had in our video on the different verb methods that we have. As you can see here, we've got a call to app.all, we've got a call to app.get and we've got a call to app.post. And all three of these calls use the very same route. Now in this case, it's just the root route, so it's nice and short. However, it's very likely that you'll have different verb methods for much longer routes. And maybe, you want to shorten that up. Because really, a route like this, these strings showing up three different times in our code, if we ever want to change that, that means we need to change it in three different places. And you've probably heard of the dry principle of software development: don't repeat yourself. Here, we're repeating that string three times. And this makes it a little more difficult to change this code in the future. So what we can do instead in Express version four is use the app.route method. The app.route method takes a single parameter, which is the route that we want to use. In this case that's just a forward slash, but like I just said, this could be something much longer. Then, this returns a route object which has all the methods you might need, the get method, the post method, the put method, the delete method, and of course, it also has the all method. And we can chain these on, as I mentioned, that we can do with the app object or of course, we could put the route in an object like that and call it the home route, and go ahead and use each of these normally. However, I'm gonna go ahead and use the chaining syntax here. And so now what we can do is use the methods that we have down here, and remove that route parameter. So I'm going to delete all these. Let me take that app object off the beginning there. And we can take this route name parameter out there. And then, this just looks like that. I'll remove that semicolon there. Just get rid of the app object right there, and let me indent all this. Again, we remove the route name, and the semicolon. And then let's do that one more time. And this is how we can tighten up our code, by removing the duplication of the actual route name. So this is the apt.route function. And then we have access to each one of our different request type functions, and we no longer have to pass that route URL as a first parameter. Each one of these knows by default what the route they're supposed to work on is, and this reduces that duplication. We can see this at work. I'll run node server, and now, you can see, we can add a name here. And this works just fine. There you go. So you can see that our application is doing exactly what it did before, even though we've refactored it to make the code much tighter. So that's a small lesson, but a very important one on using the app.route method to tighten up your Express code.